Alveolar Distractor
The new Alveolar Distractor is an internal distraction device intended for vertical bone augmentation of the alveolar ridge in the mandible and the maxilla with a deficit of in bony height and soft-tissue coverage.
The alveolar ridge deficiency can be a result of:
- Traumatic tooth and bone loss
- Resorption after dental extraction
- Periodontal disease
- Tumor resection
- Congenital deformity
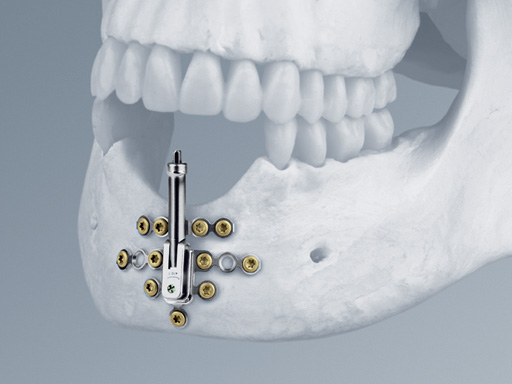
The distraction device consists of:
- The lower body with angulation mechanism which is welded to the base plate
- The upper body with distraction mechanism consisting of a threaded rod as well as a threaded transport plate.
One of the main features of the Alveolar Distractor is its vector adjustability: an angulation mechanism allows easy intraoperative selection of the distraction vector. Therefore, extensive adaptations to the foot plates can be avoided. The distractor can be angled up to 52 toward the buccal and 32 toward the lingual side. After adjusting the vector, the angulation mechanism must be relocked by tightening the fixation screw.
The rigid base plate, with optional screw holes next to the angulation mechanism, allows safe anchorage of the distraction device in the residual bone segment. This leads to high stability ensuring rigidity and preventing potential unfavorable distraction vector changes due to soft-tissue pull.
Three different implant sizes allow for 8 mm, 12 mm, and 16 mm of distraction. This choice offers the flexibility to fit the distractor to different anatomical conditions. To achieve the desired distraction result, the two bodies are connected with a pin to change the plane angle of the bone plates in one dimension. The angulation mechanism allows for fixation of this angle. This feature allows for a single, individual intraoperative adjustment of the distraction vector and addresses the importance of a correct distraction vector in a sagittal plane.
The plate is extended vertically to improve the vertical stability of the system helping to withstand lingual and palatal soft-tissue tension and therefore also guarantees a stable distraction vector. This device has housing for the distraction body to prevent soft-tissue irritation as there is no exposure of the surrounding soft tissue to the threaded rod during distraction and latency.
Distraction should begin 35 days after implantation. To achieve lengthening the activation instrument is turned clockwise (in the direction of the arrow marked on the instrument). Each full rotation equals 0.35 mm of distraction. A rate of 1.05 mm of distraction per day (one turn, three times a day) is recommended to prevent premature consolidation. After a satisfactory gain in alveolar height, the new bone must be given a consolidation period of at least 1012 weeks before the distractor can be removed through the same vestibular incisions used during implantation.
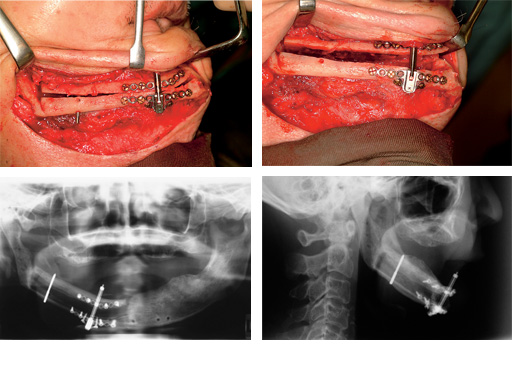
Distraction of a fibula flap in the mandibular body after tumor resection. The additional pin provides stabilization.
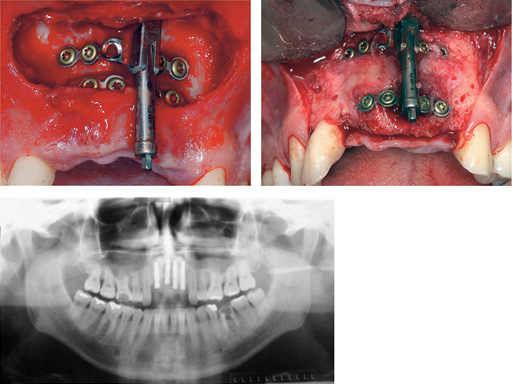
Maxillary distraction in a 34-year-old male after periodontal disease.
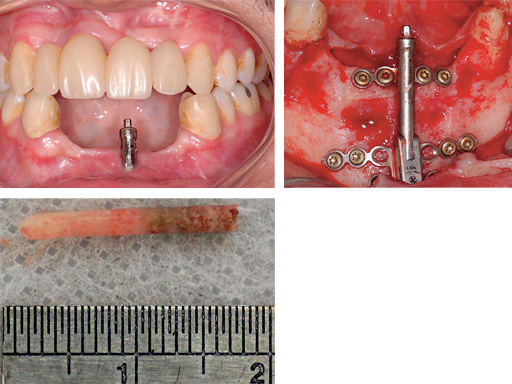
Mandibular distraction in a 20-year-old male after trauma. The bone biopsy shows a darker shading where the bone is newly formed.
Hazards and labeling
Due to varying countries’ legal and regulatory approval requirements, consult the appropriate local product labeling for approved intended use of the products described on this website. All devices on this website are approved by the AO Technical Commission. For logistical reasons, these devices may not be available in all countries worldwide at the date of publication.
Legal restrictions
This work was produced by AO Foundation, Switzerland. All rights reserved by AO Foundation. This publication, including all parts thereof, is legally protected by copyright.
Any use, exploitation or commercialization outside the narrow limits set forth by copyright legislation and the restrictions on use laid out below, without the publisher‘s consent, is illegal and liable to prosecution. This applies in particular to photostat reproduction, copying, scanning or duplication of any kind, translation, preparation of microfilms, electronic data processing, and storage such as making this publication available on Intranet or Internet.
Some of the products, names, instruments, treatments, logos, designs, etc referred to in this publication are also protected by patents, trademarks or by other intellectual property protection laws (eg, “AO” and the AO logo are subject to trademark applications/registrations) even though specific reference to this fact is not always made in the text. Therefore, the appearance of a name, instrument, etc without designation as proprietary is not to be construed as a representation by the publisher that it is in the public domain.
Restrictions on use: The rightful owner of an authorized copy of this work may use it for educational and research purposes only. Single images or illustrations may be copied for research or educational purposes only. The images or illustrations may not be altered in any way and need to carry the following statement of origin “Copyright by AO Foundation, Switzerland”.
Check www.aofoundation.org/disclaimer for more information.
If you have any comments or questions on the articles or the new devices, please do not hesitate to contact us.
“approved by AO Technical Commission” and “approved by AO Foundation”
The brands and labels “approved by AO Technical Commission” and “approved by AO Foundation”, particularly "AO" and the AO logo, are AO Foundation's intellectual property and subject to trademark applications and registrations, respectively. The use of these brands and labels is regulated by licensing agreements between AO Foundation and the producers of innovation products obliged to use such labels to declare the products as AO Technical Commission or AO Foundation approved solutions. Any unauthorized or inadequate use of these trademarks may be subject to legal action.
AO ITC Innovations Magazine
Find all issues of the AO ITC Innovations Magazine for download here.
Innovation Awards
Recognizing outstanding achievements in development and fostering excellence in surgical innovation.