ARI
Statistical analysis of complex proximal humeral fractures
Introduction
Fixation of complex proximal humeral fractures has remained challenging, partially due to the large variation in the number, shape, and displacement of fragments. Understanding the variability of fracture patterns could enhance surgical training and education and contribute to advanced implant development.
The aim of this project was to evaluate and statistically describe the pattern and spatial distribution of complex fractures at the proximal humerus.
Materials and Methods
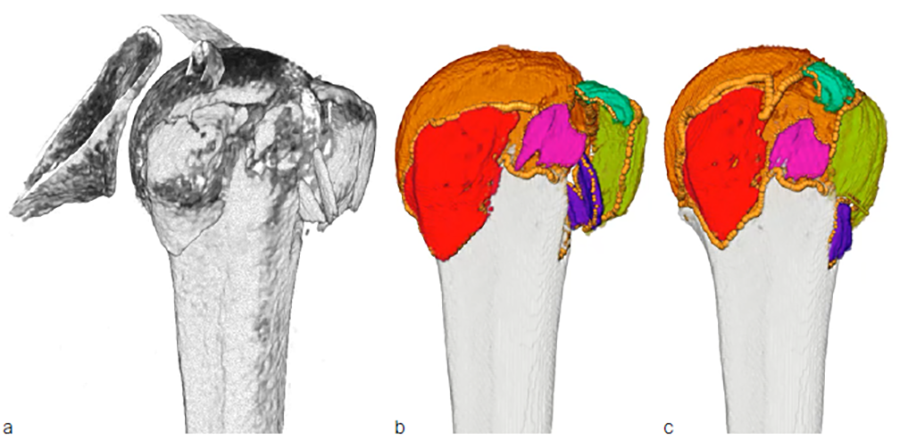
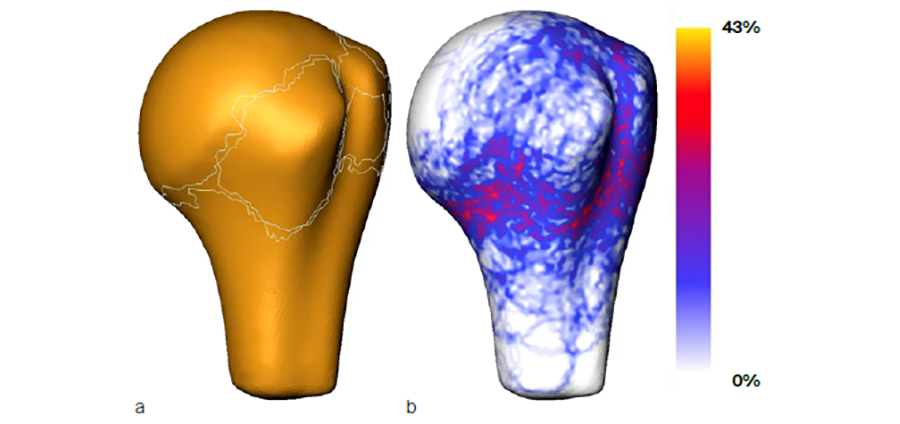
Preoperative clinical computed tomography (CT) datasets of 51 patients with three- or four-part proximal humeral fractures and intact contralateral side were collected retrospectively (Fig 1a). The fracture lines and fragments were identified semi-automatically on the CT images using advanced custom developed image processing tools (Fig 1b). Following identification, the fragments were virtually reduced by solving the 3D puzzling problem and applying the mirrored intact contralateral side as template (Fig 1c). A statistical shape model of the proximal humerus was built for this cohort of patients utilizing homologous landmarks. All individual fracture lines were projected on the averaged bone surface (Fig 2a) and their spatial variability was evaluated to indicate the most probable locations of fracture patterns (Fig 2b).
Results
The zones with highest fracture probability were identified, demonstrating a considerable scatter of the spatial distribution of fracture patterns. Enlarging the dataset with clustering of the cases is expected to provide further insights into the morphology of proximal humeral fractures that in turn can be used to design advanced implant fixation systems.
You might also be interested in
Helical plating
Provides well-balanced load sharing in laterally plated femoral defect fractures.
Pancarpal arthrodesis in canine
Although oval radiocarpal holes provide more options, they increase predicted failure risk.
Improving fixation stability with ASL
The novel TN-A delivers new approaches to treating unstable distal tibia fractures.